Melatonin vs Alternatives: Which Sleep Aid Is Right for You?
 Oct, 7 2025
Oct, 7 2025
Sleep Aid Selector
Your Sleep Challenge
Your Lifestyle
Preferred Mechanism
Select one or more ingredients that align with your preferred approach:
Melatonin
Clock-reset hormone
Valerian Root
GABA-enhancing herb
Magnesium
Muscle relaxant and melatonin aid
CBD
Anxiety-reducing cannabinoid
L-Theanine
Promotes calmness without drowsiness
5-HTP
Serotonin precursor for melatonin
Your personalized sleep aid recommendation will appear here after clicking "Analyze My Sleep Profile"
Quick Takeaways
- Melatonin is a hormone‑based supplement that helps reset your internal clock.
- Valerian root, magnesium, CBD, L‑theanine, and 5‑HTP each target sleep through different pathways.
- Safety, onset speed, and ideal use‑case vary widely - pick what matches your lifestyle and health profile.
- Start low, monitor effects, and talk to a professional if you have chronic conditions or take meds.

How Melatonin Works
Melatonin is a naturally occurring hormone produced by the pineal gland that signals darkness to the body, promoting sleep onset. When taken as a supplement, it mimics this signal, helping to shift the circadian rhythm for people with delayed sleep phase, jet lag, or shift‑work schedules.
Typical adult doses range from 0.5mg to 5mg taken 30‑60minutes before bedtime. The effect usually begins within 20‑60minutes and lasts about 4‑8hours. Because it works on the clock rather than directly sedating the brain, melatonin rarely causes next‑day grogginess when used correctly.
Side effects are mild for most users - occasional vivid dreams, slight headache, or stomach discomfort. However, melatonin can interact with blood thinners, immunosuppressants, and certain antidepressants, so a quick check with a pharmacist is wise.
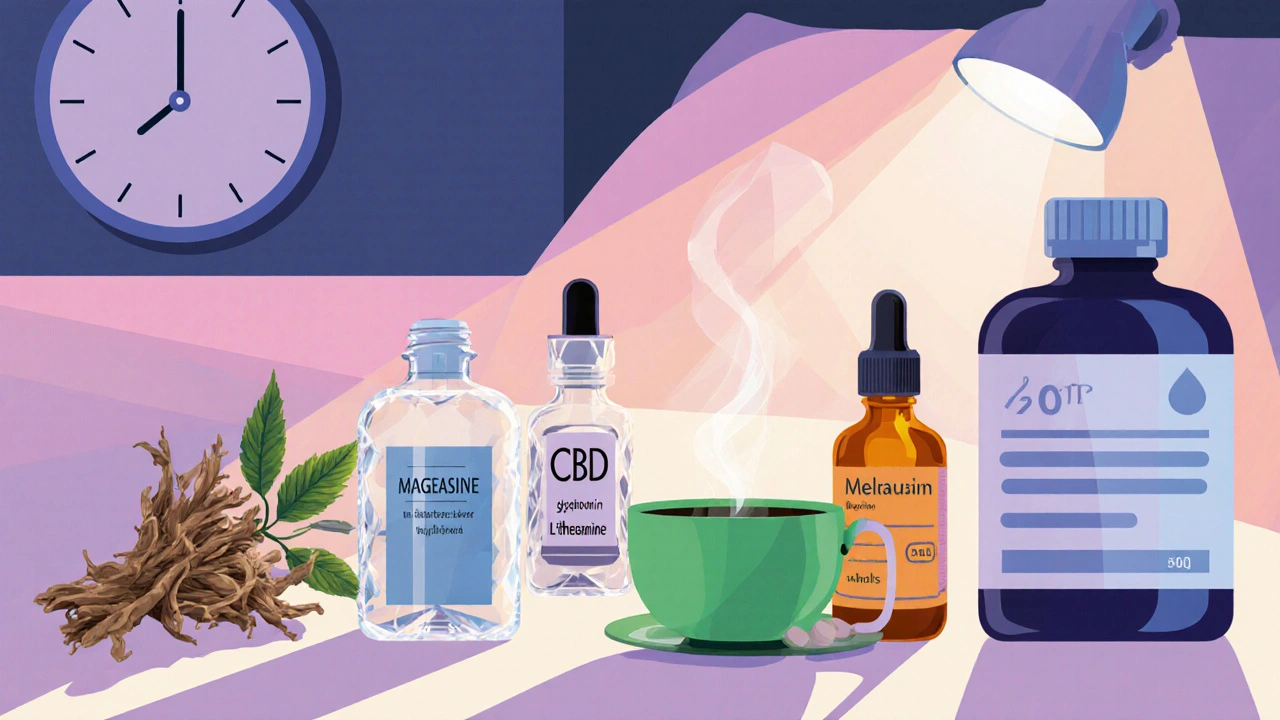
Top Alternatives to Melatonin
When melatonin isn’t enough or you want a different mechanism, several other supplements are popular. Below each is introduced with its key attributes.
- Valerian Root is a herbal extract that enhances the neurotransmitter GABA, producing a calming effect that can improve sleep quality. Typical dose: 400‑900mg, 30minutes before bed.
- Magnesium is a mineral that supports muscle relaxation and regulates melatonin production. Common forms: citrate or glycinate, 200‑400mg in the evening.
- CBD (Cannabidiol) is a non‑psychoactive cannabinoid that reduces anxiety and may modulate sleep cycles. Dosage varies widely; 10‑25mg sublingual oil about an hour before sleep is a common starting point.
- L‑Theanine is an amino acid found in tea that promotes alpha‑brain waves, encouraging relaxation without drowsiness. Recommended dose: 100‑200mg, taken with or without food.
- 5‑HTP (5‑Hydroxytryptophan) is a serotonin precursor that can raise melatonin levels indirectly. Standard dose: 50‑150mg, 30minutes before bedtime.

Side‑by‑Side Comparison
| Ingredient | Primary Mechanism | Typical Onset | Duration of Effect | Common Dose | Best For | Major Safety Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melatonin | Clock‑reset hormone | 20‑60min | 4‑8h | 0.5‑5mg | Jet lag, shift work, delayed sleep phase | Possible interaction with anticoagulants |
| Valerian Root | GABA‑enhancing herb | 30‑90min | 6‑10h | 400‑900mg | People who need deeper sleep without hormone use | May cause mild dizziness; avoid with sedatives |
| Magnesium | Mineral that relaxes muscles, aids melatonin synthesis | 45‑90min | 6‑12h | 200‑400mg | Those with muscle cramps or magnesium deficiency | High doses can cause diarrhea |
| CBD | Anxiety‑reducing cannabinoid | 15‑30min | 4‑6h | 10‑25mg | Stress‑related insomnia, night‑time anxiety | Check for THC content; may interact with liver enzymes |
| L‑Theanine | Promotes alpha brain waves | 15‑30min | 3‑5h | 100‑200mg | Light sleepers who want calm without drowsiness | Generally safe; watch for low blood pressure |
| 5‑HTP | Serotonin → melatonin precursor | 30‑60min | 5‑7h | 50‑150mg | People with low serotonin who also struggle with sleep | May cause nausea; avoid with MAO inhibitors |
How to Choose the Right Sleep Aid
Follow this simple decision flow:
- Identify the root cause. Is your problem a misaligned circadian rhythm (jet lag, shift work), anxiety, muscle tension, or a general inability to stay asleep?
- Check health conditions. Pregnancy, blood‑clotting disorders, chronic kidney disease, and mental‑health meds can narrow safe options.
- Match mechanism to need. For clock‑reset, melatonin tops the list. For calming nerves, try CBD or L‑theanine. For physical relaxation, magnesium or valerian works best.
- Start low, go slow. Pick the smallest recommended dose, use it for 1‑2 weeks, and note how you feel.
- Evaluate side effects. If you notice headaches, vivid dreams, or stomach upset, either lower the dose or switch to a different ingredient.
Remember that supplement quality matters. Look for third‑party tested brands (USP, NSF) to avoid contaminants and ensure label accuracy.

Practical Tips for Safe Use
- Take most sleep aids in a dark, cool bedroom - environment supports the supplement’s effect.
- Maintain a consistent sleep‑wake schedule; supplements work best when the body has a routine.
- Limit caffeine after 2PM and avoid heavy meals within two hours of bedtime.
- If you combine ingredients (e.g., melatonin+magnesium), keep total dose at the lower end of each range.
- Consult a pharmacist or doctor if you are pregnant, nursing, or on prescription meds such as SSRIs, blood thinners, or anti‑seizure drugs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I take melatonin every night?
Occasional use is safe for most adults, but daily long‑term use should be discussed with a healthcare professional, especially if you have hormonal disorders or are on medication.
Is valerian safe for children?
Valerian is generally not recommended for kids under 12. For younger children, a pediatrician might suggest magnesium or a low‑dose melatonin under supervision.
Which alternative works fastest?
CBD and L‑theanine often produce noticeable calming effects within 15‑30minutes, making them the quickest‑acting options for anxiety‑related insomnia.
Can I combine melatonin with magnesium?
Yes, many people stack a low dose of melatonin (0.5‑1mg) with magnesium (200mg) to cover both clock‑reset and muscle relaxation. Start with the lowest doses and monitor for any stomach upset.
Do any of these supplements cause dependency?
Melatonin, magnesium, and most herbal extracts have low dependency risk. CBD can lead to psychological reliance in a small subset of users, so it’s best used intermittently.
Sruthi V Nair
October 7, 2025 AT 17:39Interesting how melatonin resets the clock while the other herbs play with chemistry the body already has
Mustapha Mustapha
October 11, 2025 AT 04:59Exactly, you can think of it like a team where melatonin handles timing and magnesium eases tension so you get a smoother transition to sleep
Ben Muncie
October 14, 2025 AT 16:19Melatonin is best for jet lag but if anxiety is the issue CBD or L‑theanine work faster.
kevin tarp
October 18, 2025 AT 03:39Just a note: the term “herbal extract” should be hyphenated and “magnesium” is a mineral, not a supplement.
ravi kumar
October 21, 2025 AT 14:59Look, our people have used turmeric and ashghanda for ages, why are we suddenly buying imported melatonin pills?
SandraAnn Clark
October 25, 2025 AT 02:19Seems like a lot of options but most folks just need a low dose of melatonin.
Rex Wang
October 28, 2025 AT 12:39Sure, try melatonin, start low, watch effects, adjust dose, repeat.
mark Lapardin
October 31, 2025 AT 23:59From a pharmacodynamic perspective, the GABAergic activity of valerian synergizes with the circadian modulation of melatonin, offering a multimodal approach for insomnia phenotypes.
Barry Singleton
November 4, 2025 AT 11:19While the jargon sounds impressive, most users will just read the label and pick whatever looks “natural” without considering CYP450 interactions.
Kasey Lauren
November 7, 2025 AT 22:39Give yourself credit for exploring options – a small step toward better rest.
joshua Dangerfield
November 11, 2025 AT 09:59i think its cool to test melatonin first then add magnesium if you still feel tension in ur muscles
Gayatri Potdar
November 14, 2025 AT 21:19They don’t want you to know that the big pharma labs are pumping melatonin into the water supply, keep your eyes open.
Marcella Kennedy
November 18, 2025 AT 08:39When you look at the spectrum of sleep aids, it becomes clear that each one targets a distinct neurochemical pathway, and understanding these pathways is essential for personalizing therapy; melatonin acts as an exogenous cue that mimics the endogenous hormone, thereby shifting the suprachiasmatic nucleus and ultimately the whole circadian rhythm; valerian, on the other hand, potentiates GABA receptors, producing a sedative effect without necessarily aligning the internal clock; magnesium facilitates the conversion of tryptophan to serotonin and subsequently to melatonin, while also reducing neuromuscular excitability, which can be especially helpful for people whose insomnia stems from muscle tension; CBD modulates the endocannabinoid system, reducing anxiety and possibly influencing sleep architecture in ways that are still being researched; L‑theanine promotes alpha brain wave activity, yielding a calm yet alert state that can ease the transition to sleep; finally, 5‑HTP serves as a serotonin precursor, indirectly supporting melatonin synthesis, but it must be used cautiously in combination with SSRIs due to the risk of serotonin syndrome. In practice, a layered approach-starting with a low dose of melatonin for clock reset, followed by magnesium for muscle relaxation, and perhaps adding L‑theanine for anxiety-can address multiple facets of poor sleep without over‑relying on any single supplement. Remember to track your responses, keep dose low, and consult a healthcare professional if you have underlying conditions or are on prescription medications.
Jamie Hogan
November 21, 2025 AT 19:59One must appreciate the subtle elegance of a well‑timed melatonin dose, for it is not merely a pill but a synchronizing agent of the body's temporal orchestra
Ram Dwivedi
November 25, 2025 AT 07:19Happy to help! 😊 Start with 0.5 mg of melatonin 30 min before bed and add 200 mg of magnesium if you feel tight muscles. 🌙👍
pooja shukla
November 28, 2025 AT 18:39Dude, why are we even talking about foreign supplements when our own Indian herbs can do the job?
Poonam Mali
December 2, 2025 AT 05:59Honestly, this whole comparison is just a drama spin to sell more bottles. The real issue is lifestyle, not a magic powder.